Small Cells, Picocells, and Microcells: The Complete Guide
Small Cells: The Backbone of Cellular Networks
What are these strange antennas popping up all over the place?
Likely, they are small cells. Small cells are a critical part of cellular networks, especially 5G. Thus, they’ve gained lots of popularity recently, even though the technology isn’t new.
What are small cells? How do they work? Why are they popping up at an alarming rate?
First, we need to discuss what small cells are in the context of the overall cellular network.
We fix poor cell phone signal! Find the right signal booster for you:




Macrocells

Most know macrocells as cell towers. They’re large cellular base stations that provide cellular coverage for miles. However, they don’t have the capacity to keep all devices in dense towns and cities connected.
With the number of cellular devices and data demand increasing every year, towers get congested. In addition, building material and distance weaken cell reception. This prevents all users from enjoying reliable connectivity.
That’s where small cells come in. Small cells fill in the gaps, so to speak. They allow a reliable, efficient network for end users.
Small Cells
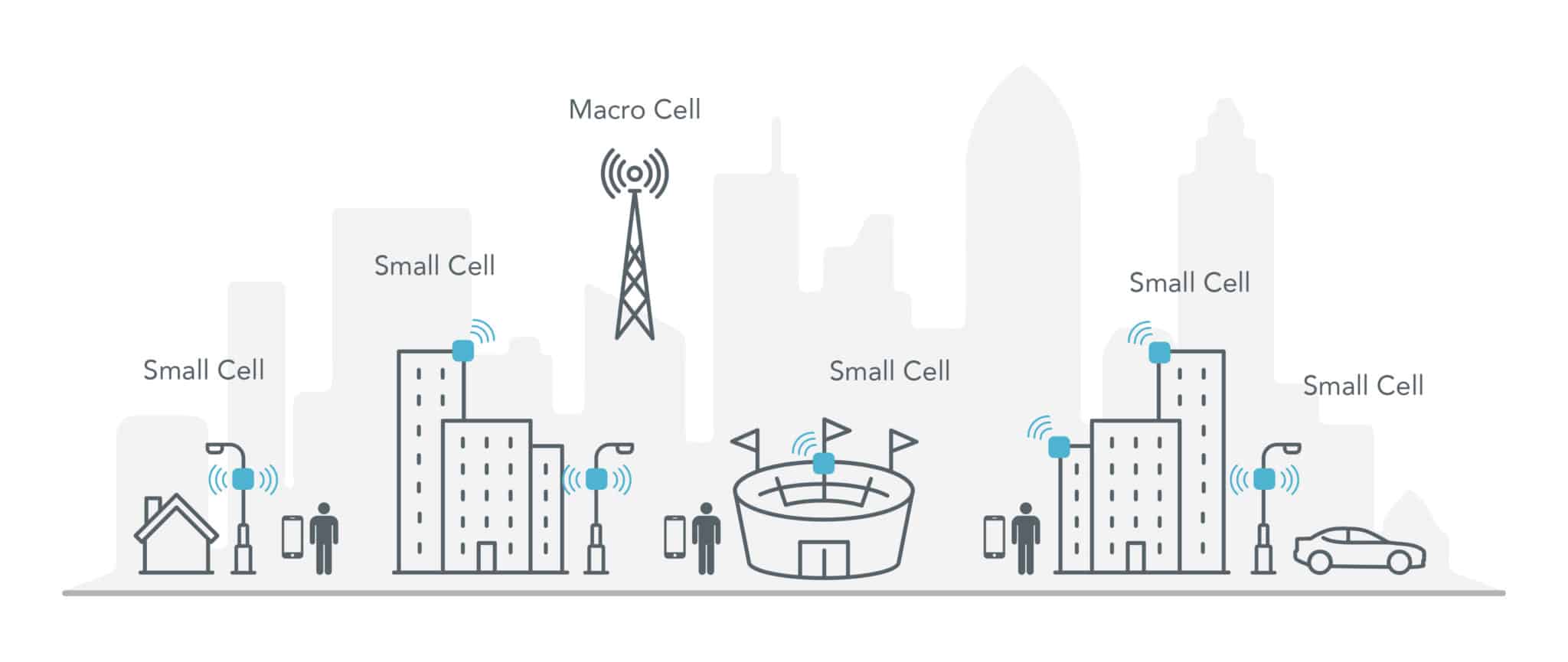
Small cells are like mini, low-powered cell towers designed to provide reliable coverage across small areas. They are densely deployed in areas where usage is typically highest to complement macrocells. Each small cell can handle multiple devices and transfer data at fast speeds.
Towns and cities don’t have to exclusively rely on large cell towers located miles apart to stay connected. Cellular signals are sent and received via multiple cell sites, improving coverage, capacity, and speed.
You’ve probably spotted some small cells, even if you don’t realize it. Small cells can be found on streetlights, sides of buildings, and other physical structures. Some small cells are even deployed in buildings. Their compact size allows carriers to cover areas with otherwise weak or no signal.
Built with smart technology, their ability to handle lots of data, and deployed so close to end users, make small cells extremely important for 5G. More on this later.
How Do Small Cells Work?
Small cells are made up of antennas (also called nodes) and carrier-specific radios. To service multiple devices no matter their carrier, multiple small cell radios are needed.
Using electrical wires, the antennas connect to the radios and the radios to the core network via fiber, wired, or microwave backhaul. Each radio needs its own backhaul.
Small cells wirelessly communicate with 4G and 5G mobile devices using low, mid, and high-frequency bands. Devices can then make calls, send texts, and access the internet.
When it comes to the transmission of high-band or mmWave 5G frequencies, small cells are vital. Since those 5G signals can’t travel far, small cells make it possible to cover cities with the fastest 5G connection.
Leveraging technologies like MIMO, beamforming, and more, small cells can deliver greater signal quality, less latency, and faster speed, for hundreds of end users.
Depending on the type of small cell used, coverage typically ranges from 30 to 8,000 ft.
Where are Small Cells Used?
There are many types of small cells with various applications. Deployable inside and outside, they can enhance coverage and capacity in residential, commercial, and metropolitan areas.
Types of Small Cells
There are three main types of small cells, each with different applications, coverage ranges, and user capacity.
Microcells
Microcells are the most powerful of small cells. They are the ones you’ll be seeing on utility poles, streetlights, and on the side of buildings. They require fiber, wired, or microwave backhaul. A single microcell can cover 8,202 ft (2.5 km) and support up to 200 devices at the same time. Built with smart tech, they can provide reliable connectivity in challenging populated areas.
Picocells
Picocells offer greater coverage of up to 820 ft (250 m) and support a maximum of 64 users. They're typically used to improve coverage and data throughput in schools, stores, and other small businesses. Though, they can also be deployed outside. They require fiber or wired backhaul.
Femtocells
Femtocells are the smallest of the three and offer the lowest power transmission. They're designed to be used inside homes and small businesses. They help improve cellular coverage indoors via fiber or wired backhaul. Coverage typically ranges from 30 to 165 feet (10-50 meters), and user capacity ranges from 8 to 16 devices at a time.
Some carriers offer femtocells to improve in-building cell reception. AT&T and T-Mobile have discontinued their femtocells. Verizon's femtocell, the LTE Network Extender, is still available, but only broadcasts 4G and LTE.
Why are Small Cells Important?
Two reasons: extended coverage and greater capacity.
While macrocells are designed to cover large areas with cellular signals, not all areas get reliable signals. Devices on the edge of the macrocells coverage will experience weaker signals than those much closer. Thick building material degrades or blocks cell signals, limiting indoor cellular connectivity. Tall structures interfere with the signal for the surrounding areas. Small cells can extend coverage to indoor and outdoor areas where cell signals have trouble reaching. All devices can enjoy a more consistent connection throughout the city or office.
Macrocells also have user capacity limitations. They aren't equipped to keep up with growing traffic and data demands. Congested macrocells result in slow speeds, higher latency, and dropped calls. Small cells offload congestion from macrocells and add network capacity to areas with high data demands. More users will receive and maintain a fast, reliable connection for work or play.
How do Small Cells Pave the Way for 5G?
5G networks aren't just about delivering faster speed for cellphones, tablets, and hotspots. It also facilitates massive IoT connectivity. To cater to different use cases, 5G uses a mix of low-, mid-, and high-band frequencies. Higher frequencies mean shorter signal range, less latency, faster speeds, and more capacity.
To ensure all 5G devices can pick up those mid-band 5G and especially high-band 5G signals, small cells are needed. Deployed close to end users, short-range 5G signals have an easier time reaching 5G devices. Plus, since higher frequencies can’t penetrate buildings well, indoor small cells help deliver reliable 5G inside.
Without small cells, those lightning-fast, ultra-low latency 5G signals wouldn't reach 5G devices. Thankfully the FCC has made it easier to deploy the necessary infrastructure for 5G connectivity.
Small Cells and Signal Boosters
Enhanced coverage and capacity indoors can be achieved with a femtocell, picocell, or signal booster. Femtocells and picocells are carrier specific, have monthly fees, and require fiber or wired backhaul. A multi-carrier solution would require multiple small cell radios, which can be pricey.
Signal boosters, on the other hand, don’t need an internet connection to work. Their signal source is nearby macrocells or microcells (if close enough). Boosters capture the provided 4G and 5G signals, amplify them, and rebroadcast them inside your building. No monthly fees. Most also support multiple carriers at the same time, so no need to purchase extra units. All devices within the amplifier’s coverage area will receive superior voice and 4G/5G data.
If you're asking yourself "Do signal boosters even work with 5G", we have the answer here.
Wilson Amplifiers is the leading provider of cell phone signal boosters. We carry multi-carrier boosters for vehicles and buildings up to 100,000 square feet. If you have any questions, don’t hesitate to call (1-800-568-2723) or email us (sales@wilsonamplifiers.com). Our signal experts are happy to help.
Sources
- How Microcells Work - Crown Castle
- Small Cells 101 – Crown Castle
- A Guide to Small Cell Technology - Telit
- What is Small Cell Technology - Verizon
- What Are Small Cells & How Do They Work? - Celona
- Small Cells - Nokia
- Indoor Small Cells – Ericsson
- Ubiquitous 5G Experiences with Small Cells - Qualcomm
- FCC Facilitates Wireless Infrastructure Deployment For 5G
Interested in Learning More? Check Out Our Signal Boosting Info Center


Money Back Guarantee

Technical Support