What are Cell Towers and How Do They Work?
Everything You Ever Wanted to Know About Cell Towers
Do you ever wonder how your phone stays connected no matter where you go? The secret behind this constant connection lies in a network of tall structures called cell towers. In this article we’ll discuss how cell towers work and everything else you might want to know.
We fix poor cell phone signal! Find the right signal booster for you:




How Do Cell Towers Work?
A cell tower, also known as a cell site, or a Base Transceiver Station, is a structure that produces a cellular signal as a “cell” in a cellular network. This is accomplished with a myriad of transceivers, digital signal processors, control electronics, primary and backup electrical power, and GPS receivers. They are, at the most basic level, radio signal transmitters.
From there, it gets much more specific to each tower. Even if you live right next to a very obvious cell tower, it might not contain transceivers that utilize frequencies for your carrier, or those transceivers might be pointed away from your location.
In general terms, cell towers use power to generate radio waves at a certain frequency. Your cell phone is tuned into a specific frequency range (or band) depending on what carrier you have and the features you’re trying to use. That’s how cell towers work.
What Components are in a Cell Tower?
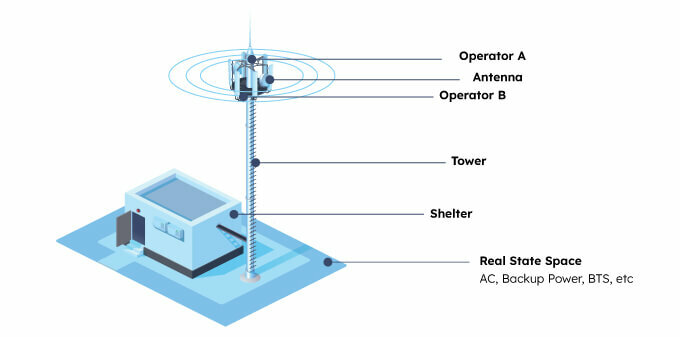
Besides the physical building, there are many components to make a complete cell tower:
- Base Transceiver Station (BTS)
- Physical Space
- Heating or Air Conditioning (or both, depending on climate)
- Equipment (antennas, etc.)
- Power
- Backup Power
- Telephone Lines (generally fiber)
- Wiring
- Fire Protection
- Planning
- Documentation
- Safety
- Commissioning
The core components of a cell tower are the radio equipment, antenna support structure, and antenna(s). The specific frequencies they use depend on the carriers occupying the tower. To keep everything running smoothly, a primary power system and a backup power or battery system are also essential, as power systems can and will fail occasionally.
Beyond the core components, cell towers require additional systems for safe and reliable operation. Air conditioning keeps equipment cool, lightning protection safeguards against potential strikes through antennas, and a fire protection system ensures overall equipment safety. Maintenance crews will need to periodically visit the sites, so you need AC power and lighting for them as well. Lastly, most cell towers are constructed to last for a long time, so space for new technology will need to be accounted for, as well as reserve capacity for every single component.
In other words, there is a lot that goes into each cell tower, and they aren’t something that anyone can just build with the right equipment: it takes a great deal of resources to make and maintain.
How Tall Are Cell Phone Towers?
Cell phone towers can vary significantly in height depending on the surrounding terrain and the coverage area. Typically, traditional or standalone towers can range from 50 to 400 feet tall.
In rural areas, where a single tower needs to cover a large area for the greatest reach, heights can reach between 150 to 300 feet. On the other hand, urban areas with many existing towers might only need shorter towers ranging between 50 to 200 feet to fill in the gaps in coverage.
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) regulations mandate that any structure exceeding 200 feet must be illuminated for aircraft safety. So, you might notice taller towers with blinking warning lights, while shorter towers don’t have them.
How Do Cell Towers Look?

A cell tower is typically a lattice structure or a steel pole. The most common design resembles a tall, vertical mast (like a giant flagpole) with multiple antenna arrays attached near the top. These antenna arrays often have a triangular or square shape and can be segmented into three or four sections facing different directions.

Cell towers can also be cleverly camouflaged to blend into your surroundings. They can be disguised as trees (usually pine or palm trees), water towers, dead tree trunks, or even flagpoles. However, if you look closely, you'll usually spot the antennas peeking out from somewhere on the structure.
How Far Do Cell Towers Reach?
The reach of a cell tower, technically called its cell radius, depends on several factors. However, a typical cell tower's usable range can extend up to 25 miles, and radio signals up to 45 miles.
In ideal conditions, with clear and flat terrain, a tower might reach the higher end of this range. However, buildings, hills, and even trees can all weaken the signal, reducing the chances of such coverage area. Urban areas with many closely spaced cell towers will generally have shorter cell radius due to signal overlap.
Is There Anything Different About 5G Cell Towers?
5G uses low to high frequencies. Higher 5G frequencies carry significantly faster data but have less reach than waves at lower frequencies.
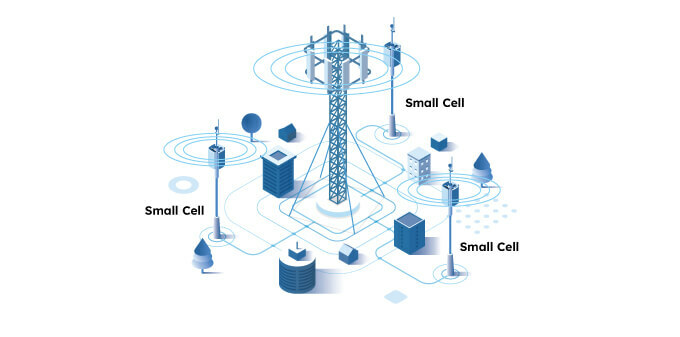
Carriers can use existing tower infrastructure to deploy low-band and mid-band 5G. However, for high-band 5G or mmWave spectrum, small cells are needed. They are small antennas deployed closer to users, typically in dense urban areas. This allows users to actually receive those ultra-fast 5G signals for the ultimate 5G experience.
Who Builds Cell Towers?
Cell towers are almost always built and maintained by large corporations that have the resources to do so.
The two main companies that build cell towers in the United States are Crown Castle and American Tower.
The main company that builds cell towers in Canada is WesTower.
These companies make money by leasing land from people, building towers there, and then leasing space on that tower to multiple carriers.
How Can I Find a Cell Tower Near Me?
There are multiple ways to find your closest cell tower. The top two methods are cell tower location websites and apps. You can read all about them and more in our comprehensive cell tower location guide.
How Can I Connect to the Nearest Tower?
Cellular devices are programmed to automatically connect to your closest cell tower powered by your carrier. Sometimes, devices can get confused and try to hold on to a weaker signal. To refresh your connection to your closest cell tower you can try restarting your phone or toggling airplane mode on and off.
Does My Carrier Own My Nearest Cell Tower?
Generally, carriers don’t own the towers they broadcast on, instead leasing space on them from companies like Crown Castle and American Tower. It’s very rare to have all major carriers on a single cell tower due to space limitations as well as competition within the cellular network space.
In short, probably not, but your tower might be.
Can I Lease a Cell Tower?
Towers are only leased to those who have usage rights on specific radio bandwidths. These are farmed out by governments and are usually presented to the highest bidder. In other words, unless you legally represent someone who has rights to one of these bandwidths, no, you can’t.
Can I Get a Cell Tower on my Land?
You can indeed. You’ll need to register with Crown Castle or American Tower if you’re in America, or WesTower if you’re in Canada, which can be done on their websites. These companies generally lease the space from landowners at a fixed monthly rate, so you can earn a fair amount from having a cell tower on your land.
There are specific cell tower regulations that need to be followed, so it's likely a representative of one of these companies will need to do a site walk on your property if you're interested in leasing the land.
- Crown Castle Landowner Registration
- American Tower Property Owner Registration
- WesTower (for Canada)
Are There Any Health Risks Associated With Cell Towers?
There is no strong evidence that exposure to radio waves emitted by cell towers causes health risks. Cell towers emit radiofrequency (RF) waves. As RF waves have the potential to heat bodily tissues, exposure to high levels of these waves can be detrimental. However, the energy levels employed by cell phone towers are far lower and are not known to cause considerable heating. Although there are unproven health impacts from low-level exposure, research is still ongoing.
As far as the real elephant in the room goes, no, there is no evidence to suggest cell towers cause cancer. Not even 5G. It’s because unlike X-rays or gamma rays, RF waves don't have enough energy to damage DNA directly. However, further research into that is ongoing.
What is a Point-to-Point?
Point-to-points (also called P2P, not to be confused with peer-to-peer) are essentially relay systems for radio waves.
Point-to-points have the advantage of creating a space in which the cellular signal is quite strong but does not create any signal itself. The disadvantage is they increase the total amount of radio “noise” in the area, which makes telecommunications projects in that place more difficult. This only really becomes an issue in certain high-traffic areas.
There are massive point-to-point stations and smaller ones. Large relays are comparable to cell towers in size but have much smaller power requirements and maintenance costs associated with them. The best cell phone signal boosters are smaller relays, with donor antennas snatching signal from the cell towers, an amplifier designed to work with common power requirements boosting the signal, and an interior antenna rebroadcasting the signal within a confined space.
Carrier Bandwidths
What Do You Know About Cell Towers?
Cell towers play a huge role in our business, so we make it a point to understand all there is to know about them.
Wilson Amplifiers is the leading provider of cellular signal boosters. While cell towers provide reliable cellular signal in many areas, there are various pockets plagued with poor connectivity, predominantly inside homes, businesses, and vehicles on remote roads or campsites. Our cell phone signal booster can help amplify and relay those signals indoors. To do so, many configurations require an antenna pointed toward your nearest cell tower for optimal performance.
Our signal experts have extensive cellular tower knowledge to educate our customers and help them get the most out of their cellular signal booster.
If you struggle with poor cellular signal or simply have questions, our signal experts are happy to help. Give us a at 1-800-568-2723 or email us at sales@wilsonamplifiers.com.
Interested in Learning More? Check Out Our Signal Boosting Info Center


Money Back Guarantee

Technical Support